Gaoma Safety Basic knowledge and methods of occupational disease prevention
Release time:
2023-09-23
As the guardian of occupational health people, Gaoma Safety since its establishment, to protect the safety and health of workers as its own responsibility, has always focused on the development and production of various safety protection products. For the basic knowledge and methods of occupational disease prevention and control, it is necessary for everyone to bear in mind, then how to achieve the prevention and control of occupational diseases? Goma Security gives you the answer!
As the guardian of occupational health people, Gaoma Safety since its establishment, to protect the safety and health of workers as its own responsibility, has always focused on the development and production of various safety protection products. For the basic knowledge and methods of occupational disease prevention and control, it is necessary for everyone to bear in mind, then how to achieve the prevention and control of occupational diseases? Goma Security gives you the answer!
(1) Strictly enforce occupational health regulations and hygiene standards
Up to now, the state has formulated and promulgated a series of labor protection laws and regulations and hundreds of occupational health standards, which are the summary of experience in practice and scientific experiments and serve as the basis for the prevention and control of occupational diseases. It must be earnestly implemented, and the implementation of supervision and inspection.

(2) Conducting preventive health supervision over construction projects
For new construction, expansion, reconstruction, technical transformation and introduction of construction projects that may produce occupational hazards, hygiene supervision and review should be carried out in the process of design, construction and acceptance according to the requirements of the "Health Standards for Industrial Enterprise Design", so that its occupational health protection measures and the main project are designed, constructed and operated at the same time. Ensure a good working environment and conditions after its operation and use.
(3) Monitoring and evaluation of occupational hazard factors in the working environment
Regularly and regularly monitor the concentration (strength) of harmful factors in the working environment, timely understand the generation, spread and change of harmful factors, identify the effect of protective facilities, and monitor the harmful substances or other metabolites in biological materials such as blood and urine of workers exposed to chemical substances and some biochemical indicators. When it is found that the concentration (strength) of harmful factors in the working environment exceeds the health standard or the content of chemical substances in biological materials exceeds the normal range, it is necessary to identify the cause and provide a basis for taking measures.
(4) Occupational health examination for workers
Workers shall be subjected to occupational health examinations before employment, at regular intervals and upon departure. In the pre-employment inspection, if it is found that there is an occupational contraindication that is not suitable for an occupational hazard factor, it shall not be arranged to engage in the contraindicated work. Regular health examination is convenient for early detection of patients, timely treatment, to prevent the development of occupational hazards, to provide a basis for the formulation of preventive measures.
(5) Establish occupational health archives and workers' individual health monitoring archives
It is the requirement of strengthening the prevention and control of occupational diseases for enterprises to set up the archives of occupational health and individual workers' health monitoring. The occupational health archives mainly include the basic situation of the work unit, the setting, operation and effect of occupational health protection facilities, the monitoring results and analysis of the concentration (strength) of occupational hazard factors, the organization of occupational health examination and the inspection results and evaluation. The personal health records of workers mainly include the contact history of occupational hazards, the results of occupational health examination, the diagnosis, treatment, treatment and recuperation of occupational diseases, and the rescue situation of occupational hazards accidents.

(6) Eliminate occupational hazards and improve working conditions
1. Prohibit the production, import and use of internationally prohibited substances that pose a serious risk to human health. Such as benzidine, β-naphthylamine and other strong carcinogens and organic mercury pesticides.
2. Improve working methods to reduce the dissemination of harmful factors.
3. Strengthen the maintenance and management of equipment to reduce the running, bubbling, dripping and leaking of toxic substances.
4. Improve the environmental health of the workplace and eliminate the secondary pollution of harmful substances.
(7) Rational use of effective personal protective equipment
When the concentration (strength) of harmful factors in the workplace is higher than the national health standards, or when it is necessary to contact high concentration (strength) of harmful substances due to equipment maintenance, effective personal protective equipment must be equipped.
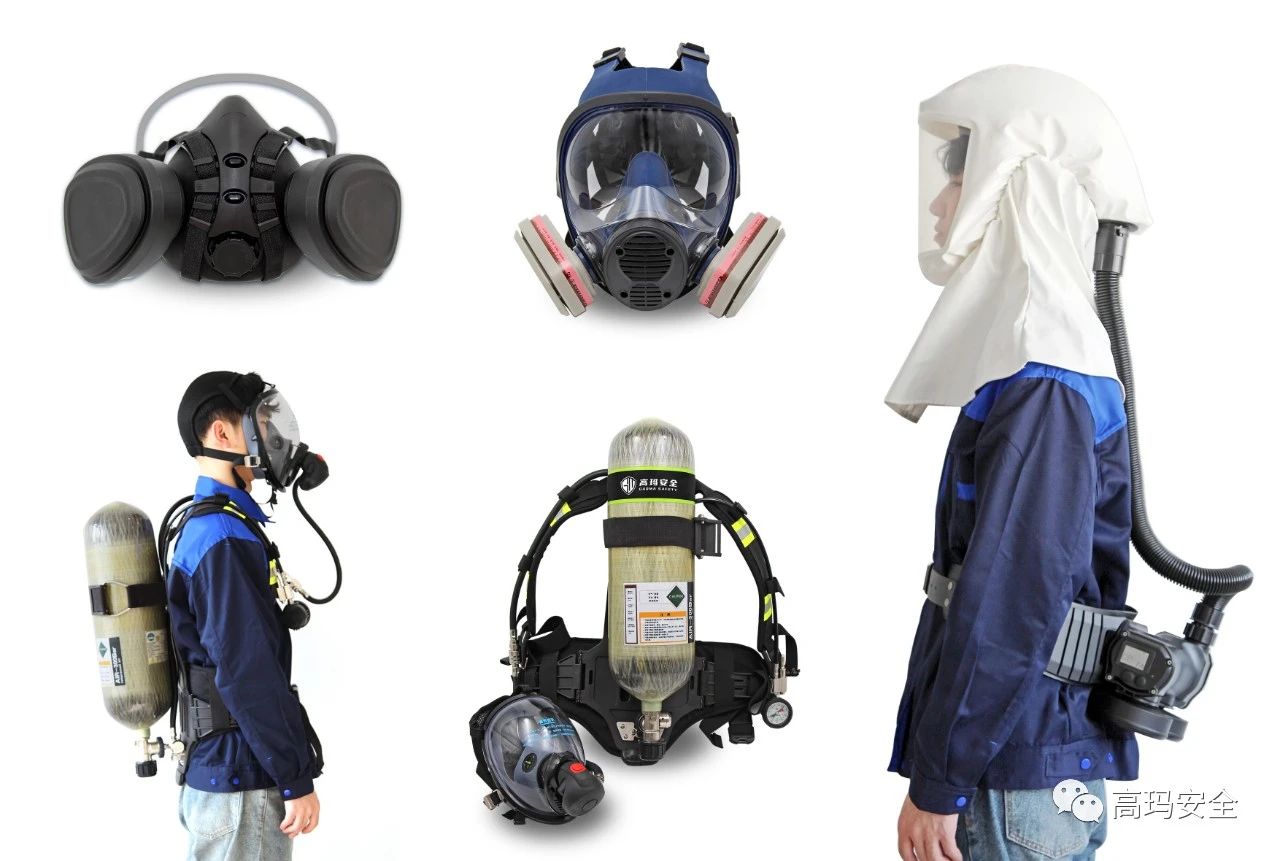

(8) Pay attention to personal hygiene, rationally arrange work and rest, and pay attention to the combination of work and rest.
(9) Special protection shall be given to young people and women workers.
Minors shall not be arranged to engage in work exposed to occupational hazards. Women workers during pregnancy and lactation shall not be assigned to work that is harmful to themselves and the fetus.
(10) To carry out health education, popularize protection knowledge, and formulate occupational health systems and operating procedures.
The leaders and workers of the employer shall, through training, learn the policies and regulations on the prevention and control of occupational diseases, occupational hazards and their protection knowledge. Raise awareness of the importance of improving working conditions and controlling occupational hazards to prevent the occurrence of occupational diseases.
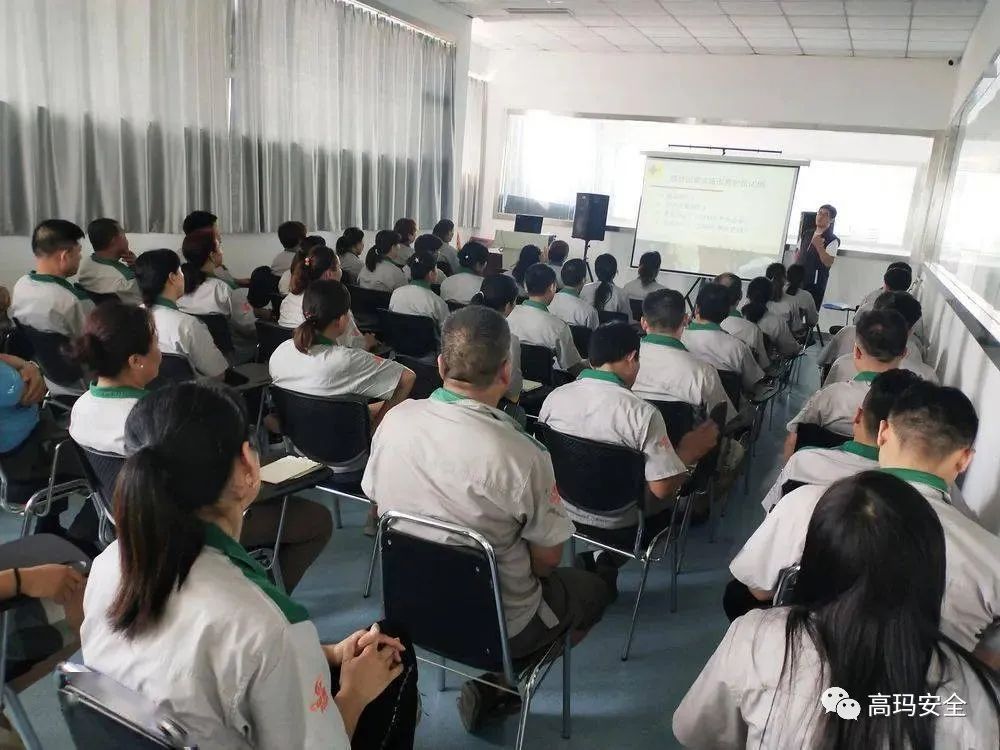

(11) Diagnosis of occupational diseases
The diagnosis of occupational diseases should be based on the following principles:
1. Have a clear occupational history, monitoring data of harmful factors in the working environment and biological monitoring data.
2. The results of symptoms, signs and routine laboratory examinations, physical examinations, biochemical examinations and other auxiliary examinations have a clear causal relationship with the occupational hazard factors exposed.
(12) Treatment of patients with occupational diseases
After the diagnosis of an occupational disease, according to the diagnosis results of the occupational disease diagnosis institution, treatment should be carried out according to the following principles:
1. Prevent harmful factors from continuing to invade the human body.
2. To promote the absorption of harmful factors out of the body.
3. Eliminate the cause.